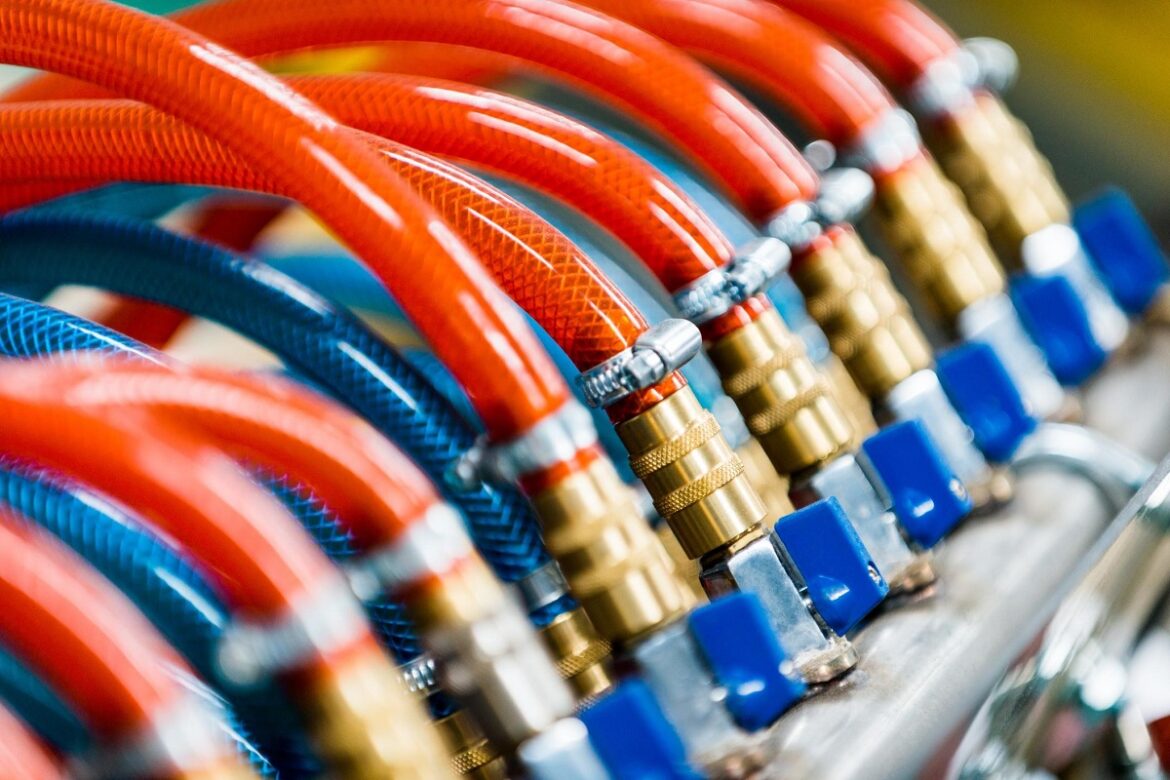
We live in a world where machines and automation play an increasingly important role. One form of automated machine technology is fluid power, which harnesses the potential of hydraulic and pneumatic systems to unleash powerful forces capable of doing tremendous amounts of work.
From performing complex manufacturing processes to lifting heavy objects with ease, fluid power has become an essential component in modern-day life. But what exactly is it? How does it work? And why is it so powerful? In this article, we’ll explore the fascinating world of fluid power and uncover the magic behind these incredible systems.
Introduction to Fluid Power: How Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems Work

Source: nfpafoundation.org
Fluid power is a type of technology that transforms stored energy into usable mechanical work. Through the use of pressurized fluids, such as air or oil, fluid power systems can generate powerful forces capable of lifting heavy loads, moving large distances quickly, and controlling complex machines.
This article will introduce you to the fundamentals of pneumatic and hydraulic systems – two types of fluid power in common use today – and explore how they work. Pneumatics are powered by compressed air which is used to create linear motion by pushing against a piston within a cylinder.
The pressure created from compressing the air forces the piston down inside the cylinder causing it to move linearly. When connected with other components like valves and actuators pneumatics can be used for sophisticated control applications such as robotic arms on manufacturing lines or automated production machinery.
Hydraulics are powered by liquids such as water or oil that is converted into linear motion through an intricate system comprised of pumps, cylinders, motors, reservoirs, hoses & fittings – all working together under controlled pressure levels. Hydraulics have been around for centuries but modern technology has allowed engineers to develop these systems so they can operate more efficiently at higher pressures making them suitable for countless applications ranging from construction equipment to industrial robotics & machine tools.
Benefits of Using Fluid Power Systems
Fluid power systems have revolutionized the way that machines and equipment can operate, allowing for increased precision, efficiency, and reliability. With pneumatic or hydraulic systems, businesses are able to reduce their overall energy consumption while still meeting production goals.
Additionally, these systems require less maintenance than traditional methods of powering machinery due to their low moving parts count and lack of wear-and-tear associated with electric motors. The advantages don’t stop there either – fluid power systems offer improved safety features with higher levels of control over hazardous processes as well as enhanced operator comfort due to reduced vibration from operating machinery.
The use of fluid power also enables faster response times in motion control applications which can be invaluable when it comes to automation tasks such as machine loading/unloading or packaging materials. Finally, this type of system is extremely cost-effective; the initial setup may be more expensive but the long-term benefits far outweigh any upfront costs associated with installation.
The Different Types of Fluid Power Systems

Source: cedengineering.com
Fluid power systems are a type of mechanical technology that is used in many different industries for a variety of applications. Broadly speaking, there are two types of fluid power systems: pneumatic and hydraulic.
Both use pressurized fluids to generate force and motion, but they work very differently from each other. Pneumatic systems rely on the compression of air or gases to generate force.
Compressed air is stored in tanks, where it can be released into cylinders or motors through valves when needed. This allows for precise control over the amount of force generated, making them ideal for tasks requiring exact movements such as robotics or automated machinery operations.
In contrast, hydraulic systems use liquids (most commonly oil) instead of gases to create movement and pressure. They operate using pumps that push fluid from one area to another within sealed pipes or tubes at high pressure levels so as to transfer energy throughout the system more efficiently than compressed gas can achieve alone.
Conclusion
Fluid Power systems are a powerful technology that can be used in many different applications, from industrial machinery to aircraft and even medical equipment.
The possibilities for using pneumatic and hydraulic systems are almost limitless, offering engineers an unprecedented level of control over their machines and the ability to create unique solutions tailored to specific needs. With more companies recognizing the potential of this innovative technology, it’s easy to see why fluid power has been unleashed as an unstoppable force in modern engineering.